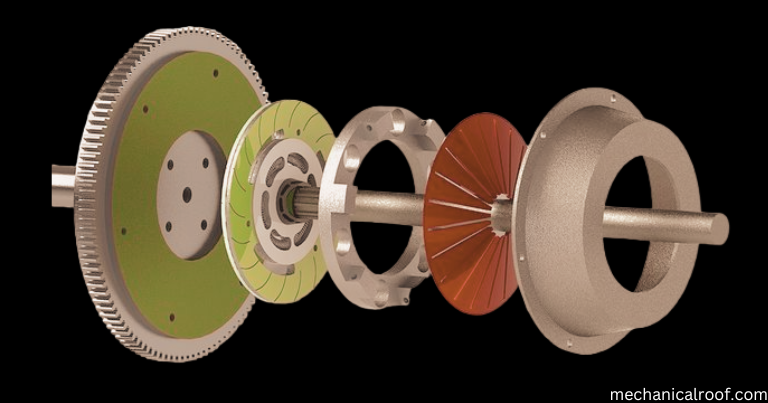
What Is A Single Plate Clutch?
Single Plate clutches are the most not unusual form of clutch disc utilized in automobiles. It includes handiest one grab disc, that’s attached to the splines on the seize disc. The flywheel is attached to the engine crankshaft and rotates with the engine.
The seize consists of two major parts, one attached to the enter shaft and the alternative connected to the output shaft.
These waves are parallel and concentric with every different. The riding torque may be increased with the aid of increasing the powerful contact radius.
Working Of Single Plate Clutch
When the engine is jogging and the flywheel rotates, the pressure plate additionally rotates as it’s far linked to the flywheel. The friction disc is among the flywheel and the stress plate. The grasp is disengaged whilst the riding force is pressed down.
The strain plate is bolted to the flywheel via the grasp spring and might slide (flow) freely on the clutch shaft while the clutch pedal is depressed (engaged and disengaged).
When the take hold of is engaged
- When the grasp is engaged (grab pedal now not pressed), the grasp disc is sandwiched among the flywheel and the stress plate.
- The seize disc rotates the flywheel due to friction between the flywheel, grab disc and strain plate.
- The clutch shaft additionally rotates with the grab disc.
- The engine’s power is transmitted to the crankshaft after which to the clutch shaft and gearbox.
When the take hold of is disengaged
- When the clutch is disengaged (while the take hold of pedal is pressed), the stress plate actions again towards the force of the spring and the take hold of disc among the flywheel and the stress plate is launched.
- The flywheel constantly rotates with the crankshaft. The seize shaft then slowly slows down and prevents rotating.
Single Plate Clutch Diagram
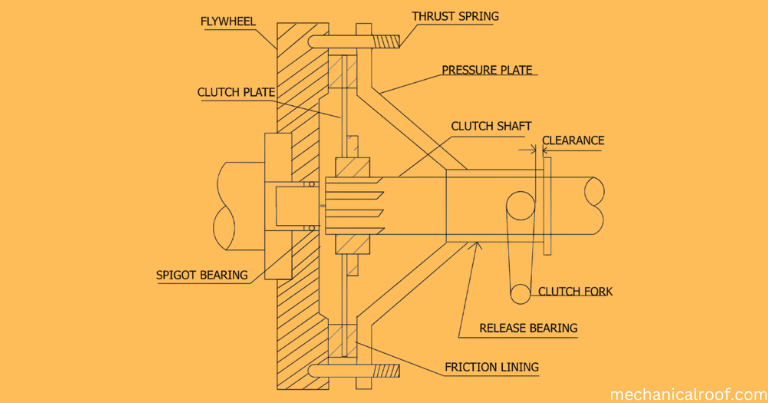
Parts Of Single Plate Clutch
A single plate clutch for electricity transmission consists of a flywheel, a seize disc, a strain plate, a seize cowl, a launch lever, and a number one shaft or clutch shaft.
- Flywheel
- Pilot Bearing
- Clutch plate or Disc plate
- Pressure plate
- Clutch cover
- Release levers
- Clutch shaft
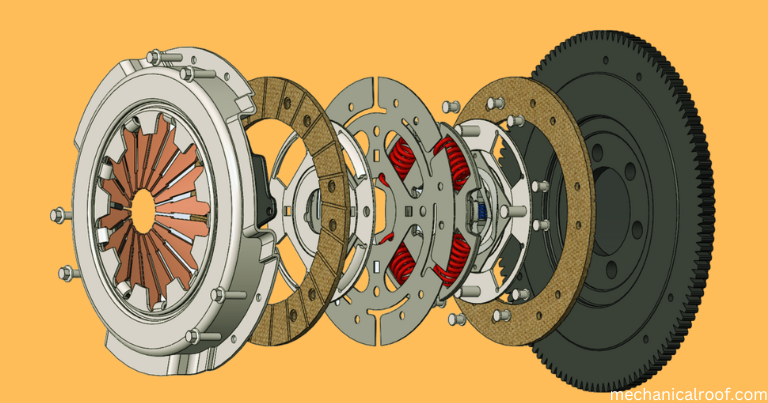
1) Flywheel
The flywheel is an fundamental a part of the engine and is likewise used as a part of the take hold of. It is the riding element linked to the strain plate of the clutch shaft and housed in a bearing flywheel. The flywheel rotates when the engine crankshaft rotates.
2) Pilot Bearing
The pilot bearing or pilot bushing is press-outfitted into the end of the crankshaft and supports the stop of the transmission input shaft. The pilot bearing prevents the transmission shaft and clutch disc from rattling up and down when the clutch is disengaged.
3) Clutch disc or disk disk
It is the driven element of a single plate clutch and line with friction material on both sides. It has a relevant hub with inner splines which restriction the axial motion along the splined input shaft of the transmission.
It facilitates in damping measures towards torsional vibrations and using torque fluctuations between the engine and transmission.
A clutch disc is a plate that’s between the flywheel and the friction plate or pressure plate. There are a sequence of pad inverters on each sides to boom friction. These grasp linings are made of asbestos material. They are distinctly resistant to wear and heat.
4) Pressure Plate
Pressure plate is made from unique solid iron. It is the heaviest a part of the take hold of meeting. The major feature of the strain plate is to provide uniform touch with the driven plate floor in order that the compression spring can exert enough force to transmit the whole torque of the motor.
The pressure plate presses the machined floor of the seize disc against the flywheel. A compression spring is set up among the strain plate and the seize cover meeting.
When the discharge lever is pushed by using the toggle lever or circled as a result, strain is eliminated from the flywheel.
5) Clutch Cover
The grasp cover meeting is bolted to the flywheel. It consists of a stress plate, release lever mechanism, clutch cover and compression spring. Normally the seize plates rotate approximately the flywheel.
However, when the take hold of is disengaged the flywheel and pressure plate rotate freely independent of the pushed plate and power shaft.
6) Release Levers
These are attached to pins inside the seize cover whose outer ends locate at the legs of the strain plate and whose internal ends challenge toward the clutch shaft.
Careful and correct adjustment of the release mechanism is one of the maximum vital factors in the performance of the grasp meeting.
7) Clutch shaft
It is part of the transmission. It is a splined shaft on which the hub of the clutch disc slides. One stop of the clutch shaft is hooked up to the crankshaft or flywheel and the other cease is connected to or paperwork a part of the transmission.
Types Of Single Plate Clutch
- Single Plate Clutch with Coil Spring
- Single Plate Clutch with Diaphragm Spring
1. Single Plate Clutch with Coil Spring
For comfort, the clutch pedal and other connections which motive the movement of the strain plate were overlooked. As proven.
The seize disc is established on a splined shaft and can pass along the shaft axis. As some distance as the rotational movement is worried, there’s no relative movement between the disc and the shaft. Due to the splines on the shaft, each have the same rotational motion. The flywheel is hooked up to the engine crankshaft and rotates with the engine. The strain plate is bolted to the flywheel through the clutch spring. It is loose to slip alongside the axis of the coupling shaft.
The seize is engaged by using the force of the seize spring. This pressure brings the pressure plate, take hold of plate and flywheel into contact. The snatch disc is located between the flywheel and the stress plate. The take hold of disc has friction cloth on both facets.
Rotational movement from the flywheel is transferred through friction to the clutch disc and grab shaft. The snatch shaft additionally acts as the output shaft.
Clutch The grasp is “disengaged” whilst the pedal is depressed. The pressure plate moves again against the pressure of the spring and the seize disc is launched between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
In different words, so long as the engine is going for walks, the flywheel continues to rotate, however the velocity of the take hold of disc slows right down to 0. In this case, no motion is transmitted to the grab shaft.
2. Single Plate Clutch with Diaphragm Spring
This sort of snatch makes use of a single diaphragm spring, a dish-fashioned disk, as opposed to a coil spring. When the seize is engaged, the disc turns into flat. In the disengaged function, the disc has a curved shape as shown within the diagram.
This diagram suggests the grasp in the “engaged” position. The diaphragm spring exerts a force on the strain plate, causing the strain plate, grasp disc, and flywheel to touch.
When the grasp pedal is pressed, the diaphragm spring deflects, inflicting the pressure plate, grasp disc, and flywheel to lose contact. The take hold of is disengaged and no longer transmits flywheel motion to the grasp shaft.

Application Of Single Plate Clutch
The application areas of single plate snatch are as follows:
- Single disc clutches are used wherein there’s sufficient radial area.
- This sort of coupling does no longer require any lubricant for cooling.
- Single plate clutches do not require any cooling oil as they’ve enough heat dissipating floor place. Hence single plate clutches are dry clutches.
- Most vehicles use unmarried plate clutches because of the high coefficient of friction. The coefficient of friction is above zero.3.
Advantages Of Single Plate Clutch
The major benefits of this seize are:
- Single plate clutches operate easily. H. The grab engages and disengages smoothly.
- There is almost no slippage whilst driving. Slippage occurs best whilst the grasp is engaged, and then there may be no slippage and it turns into very clean.
- Power loss is very low.
- As only one take hold of disc is used, little or no warmness is generated.
- This type of clutch is operated very quickly.
Disadvantages Of Single Plate Clutch
The principal negative aspects of this take hold of are:
- Single disc clutches enjoy higher levels of wear and tear.
- They have lower torque transmission ability.
- The springs want to be stiffer and consequently extra force is required to disengage.
- It calls for extra preservation.
- It calls for greater space for the grasp in comparison to multi-plate grab.
Related FAQ’S
What is a single disc clutch?
Single disc clutches have one seize disc. They work on the friction precept. They are the most not unusual kind of take hold of used in vehicles. They consist of two foremost components: one that is attached to the enter shaft and the alternative this is attached to the output shaft.
What are the elements that a unmarried plate snatch consists of?
Parts of a unmarried plate take hold of:
1. Flywheel
2. Guide bearing
three. Clutch disc or disc plate
4. Pressure plate
5. Clutch cowl
6. Release lever
7. Clutch shaft
What are the forms of single plate clutches?
Single plate clutches have one clutch disc and work on the precept of friction. There are types: coil spring and diaphragm spring. In a coil spring seize, the coil spring is frivolously allotted across the cross segment of the strain plate and exerts an axial pressure.
Where is a single plate clutch used?
In a single plate take hold of, a friction disc (clutch disc) is sandwiched among the flywheel and the strain plate. Single plate clutches are used to transmit smaller powers than multi-plate clutches. Single-plate clutches are utilized in vans, passenger cars, buses, and so on.
What is the difference among a single-plate take hold of and a multi-plate clutch?
As the name suggests, a single-plate seize is a clutch in which friction material is coated on each facets of the take hold of disc. A multi-plate snatch is made up of multiple clutch discs. The transmission torque potential will decrease.