What Is A Lever?
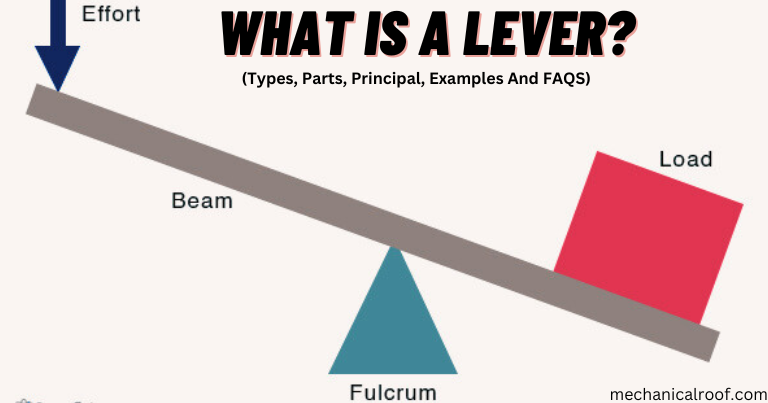
A lever is an honest mechanism that consists of a hard and fast hinge or fulcrum and a beam or rigid rod, that is used to transfer force to a load and provide a mechanical advantage. It is an inflexible body that can rotate around a factor on itself. Depending on the position of the fulcrum, load, and effort, levers may be labeled into three sorts. Furthermore, leverage refers back to the gain received by using a lever in a gadget.
This simple gadget is fantastically effective for lifting or moving heavy items, making it a generally used device observed in diverse settings. Some main examples of levers encompass the seesaw, fishing line, oars, wheelbarrows, crowbar, and the garden shovel. Levers also one of the 6 simply machines identified by Renaissance scientists. By amplifying an enter force, levers offer an extra output pressure, which is known as leverage.
The mechanical advantage of a lever is determined with the aid of the ratio of the output force to theenteringr pressure. In essence, levers are machines that increase pressure and are categorized as ‘simple machines‘ because they encompass only two components – the deal with (or arm) and the fulcrum. The cope with is the part that is pushed or pulled, at the same time as the fulcrum is the point on which the lever rotates or balances.
As such, levers are considered mechanical gain devices as they trade forces for motion. The mechanical gain of a lever can be calculated by the usage of the formula Load/Effort. This simple device has been used considering historic times, with evidence of its use in Egypt and IIndia’srelationship again to 1500 BCE, in which it was used for lifting water and squaddies during wars.
Types Of Lever
There are 3 distinct classes of levers, 1st-class, 2nd-class, and 3-class, which range primarily based on the positioning of the force, fulcrum, and load.
- First Class Lever
- Second Class Lever
- Third Class Lever
1. First Class Lever
The fulcrum is positioned among the force and the burden in high-quality levers. When using a screwdriver to open a paint tin, the effort is implemented over an extended distance in comparison to the burden. Placing the fulcrum (the rim of the tin) close to the lid (the load) lets in for an extra force to be exerted on the load, making it simpler to open the tin.
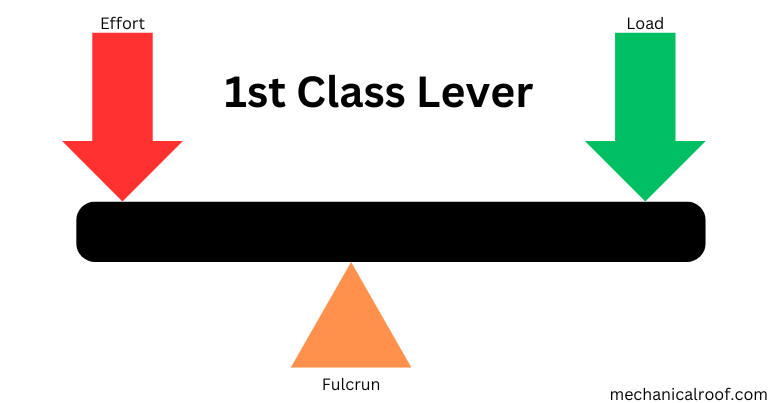
This showcases the principle characteristic of quality levers, which is to lessen the effort required. Pliers, scissors, a crowbar, a claw hammer, a see-saw, and a weighing balance are different examples of pleasant levers. In precis, a nice lever includes the effort (pressure) transferring a bigger distance if you want to pass the burden a shorter distance, with the fulcrum between the effort (force) and the burden.
The mechanical advantage of an excellent lever will increase because the ratio of effort (force) arm duration to load arm duration increases. This idea was famously referenced by Archimedes who stated, ‘Give me one company spot on which to relax (a fulcrum) and I will move the Earth.’
2. Second Class Lever
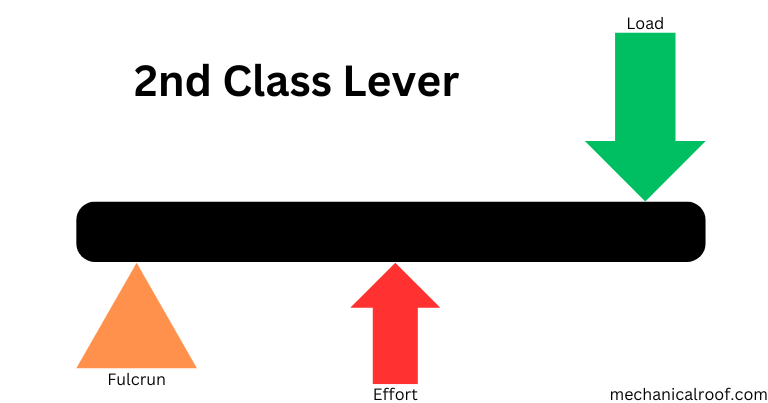
The load is positioned between the effort (force) and the fulcrum in 2d-magnificence levers. An illustration of that is visible in a wheelbarrow, in which the attempt is carried out over a large distance to raise a heavy load, the usage of the axle and wheel because of the fulcrum. In 2nd-class levers, the burden is raised a small distance as the effort moves over a bigger distance.

The mechanical gain of a second-class lever increases because the ratio of effort arm period to load arm length will increase. A wheelbarrow demonstrates this precept as the mechanical advantage is more when the load is towards the wheel. Another example of a 2nd-class lever is a nutcracker.
3. Third Class Lever
In gadgets consisting of barbeque tongs, the effort in a 3rd-magnificence lever is placed between the load and the fulcrum. Other times 1/3-magnificence levers consist of a broom, a fishing rod, and a woomera. In this type of lever, the weight moves a greater distance than the effort, resulting in a low mechanical benefit and making it difficult to exert a large force on the load. However, this may be useful in preventing the squashing of sausages at the barbeque.
When utilizing your forearm to boost a load, you are correctly the usage of a third-class lever. The biceps muscle tissues are related to the forearm simply in the front of the elbow, wherein the attempt is placed among the fulcrum (elbow) and the load (hand).
Parts Of A Lever
There are 3 parts of a lever
- The fulcrum, is the pivotal factor around which the lever rotates.
- The input pressure, also referred to as the attempt, is the force that is exerted on the lever.
- The output force, additionally referred to as the weight, is the force that is generated with the aid of the lever to move the load.

Lever
A beam is a lengthy plank crafted from wooden, steel, or any other strong substance that rests on a fulcrum, developing a pivot factor. When one gives up the lever is pressed down, and a force (input) is carried out. The lever then pivots at the fulcrum and produces an output (lifting a load) with the aid of exerting an output force on the load. By growing your enter pressure and changing its route, a lever simplifies work.
Principal Of Lever
A lever features by reducing the amount of pressure required to transport an item or elevate a load. This is completed by growing the gap over which the pressure acts. Instead of exerting a concentrated effort over a short distance, a lever spreads out the effort over an extended distance, making the work easier.
Practical experiments have shown that after identical forces are implemented in contrary instructions at identical distances from the fulcrum of a uniform lever, they stabilize each other and create a kingdom of equilibrium. Furthermore, it’s been noted that two unequal forces also act in contrary directions, and the value of one force may be decided by multiplying the value of the alternative force with its effort arm or lever arm. This concept, called the theory of moments, states that equilibrium is completed whilst the sum of the moments of the forces appearing in a counterclockwise direction is the same to the sum of the moments of the forces performing in a clockwise course.
In the sphere of physics, the fabricated from a force and its effort arm is known as the instant of force. This precept allows us to triumph over a massive force at a distance by the usage of a smaller force at a greater distance from the fulcrum. Legend has it that Archimedes possessed a lever in his thoughts, which furnished him with an area to face and flow the arena.
If you are nevertheless uncertain about the function of a lever and the way it operates, let’s break it down into easier components for a piece of higher information.
Examples Of Levers
Everyday life provides numerous instances of levers, which include teeter-totters, wheelbarrows, scissors, pliers, bottle openers, mops, brooms, shovels, nutcrackers, and diverse sports activities systems like baseball bats, golf golf equipment, and hockey sticks. Additionally, the human arm can also characterized as a lever.
First-Class Lever Examples
The first form of lever that is widely known is the seesaw or teeter-totter, which operates as a first-order lever. The pressure exerted by using a rider sitting at one stop of the seesaw is transferred through the fulcrum, inflicting the rider at the opposite cease to be lifted. By shifting the fulcrum toward a heavier rider, the pressure from a lighter rider can have more effect.
Another instance of a first-order lever is scissors, which can be generally used for slicing. The handles function as the factor of effort, even as the screw that connects the 2 blades acts because of the fulcrum. The force applied to the handles is translated to the blades, letting them reduce through cloth.
Similarly, pliers are also characteristic of first-order levers. The handles are used to use pressure, at the same time as the hinged middle serves because of the fulcrum. The resistance or load happens between the enamel of the pliers, permitting them to grip and control gadgets.
Second-Class Lever Examples
A second-order lever, together with a wheelbarrow, has a wheel as the fulcrum and the applied pressure on the handles, with the burden between them. Similarly, a classic handheld nutcracker is also a 2d-order lever, with the hinged cease because the fulcrum and the pressure implemented at the handles to crack the nut (load). Another instance is a handheld bottle opener, which capabilities as a second-order lever, with the force applied at one quit to conquer the resistance of the bottle cap, and the fulcrum at the other quit resting on the bottle cap.
Third-Class Lever Examples
Many kinds of wearing systems, consisting of baseball bats, golf equipment, and hockey sticks, can be labeled as 0.33-order levers. When the usage of those items, one hand serves as a pivot factor whilst the opposite hand exerts a greater force. This lets in the force to be transferred to the alternative end of the item, along with a baseball, golf ball, or hockey p.C.
Similarly, when lifting an item like an apple, your arm functions as a third-order lever. The elbow acts because the fulcrum, the muscle tissues offer the carried out pressure, and the item is lifted.
In the case of a shovel, the hand closest to the cease of the deal acts as the fulcrum, at the same time as the other hand exerts an attempt to transport the burden. This reason the shovel quit to boost and flow the burden.
Even family gadgets like brooms and mops may be taken into consideration 1/3-order levers. In this case, the top hand serves as the fulcrum, the decreased hand offers the force, and the broom or mop gives up and pushes toward the resistance of the dirt and ground.
Uses Of Lever
Levers are normally utilized for the reason of relocating or hoisting objects. Occasionally, they’re hired to use strain in opposition to objects without moving them. By exerting a discounted force over an extra distance at one stop, levers can exert a good-sized force over a short distance at the other cease.
Uses of Lever:
- Levers are beneficial tools for lifting heavy gadgets, loosening tight gadgets, and slicing through materials.
- One not unusual type of lever is the hammer claw, which is designed mainly for getting rid of nails from wood or other difficult surfaces.
- Another normal utility of levers is the wheelbarrow, which permits for easy transportation of heavy hundreds.
- Tweezers and pliers are examples of levers that make it feasible to boost or put off gadgets quite simply, no matter their weight.
- Scissors additionally utilize the principle of levers to use force and reduce or separate substances.
Related FAQ’S
What Is A Lever?
Answer: Levers are machines used to boom force. We call them “simple machines” due to the fact they have got most effective two elements, the take care of, and the fulcrum. The manage or bar of the lever is called the “arm”, it’s the part that you push or pull on.
What Are The Types Of Levers?
Answer: There are 3 varieties of levers.
1. First-class lever – the fulcrum is inside the center of the effort and the burden. First-elegance lever.
2. Second elegance lever – the weight is in the middle between the fulcrum and the effort. Second class lever.
3. Third magnificence lever – the effort is inside the center between the fulcrum and the weight.
What Is A First-Class Lever?
Answer: In summary, in a great lever, the attempt (force) moves over a large distance to transport the burden a smaller distance, and the fulcrum is between the attempt (pressure) and the burden. As the ratio of effort (pressure) arm period to load arm duration increases the mechanical advantage of a first-class lever will increase.
What Is A Second-Class Lever?
Answer: In a 2nd-elegance lever, the effort moves over a large distance to elevate the burden a small distance.
What Is A Third-Class Lever?
Answer: In a third-class lever, the burden moves similarly than the effort (pressure) and the mechanical benefit is low, that’s why it’s hard to apply superb force to the weight. This can be an advantage with the aid of not squashing sausages at the barbeque!
What is the essential concept behind the lever?
Answer: The principle of the lever states that when same forces are implemented in opposite instructions at the same distances from the fulcrum on a uniform lever, they create a kingdom of equilibrium or balance.
What is the governing rule of the lever?
Answer: The Law of the Lever is expressed as ( E ) ( R ) = ( L ) ( r ), wherein E is the attempted force, R is the lever arm related to the effort, L is the weight, and r is the lever arm related to the load. Essentially, the product of the lever arm and the force is equal for each effort and the load.
What are the primary programs of the lever?
Answer: Some examples of the uses of the lever are:
- Wheelbarrow
- Staplers
- Doors or gates
- Bottle openers
- Nutcracker
- Nail clippers
What are the three most important kinds of levers?
Answer: The three varieties of levers are labeled as:
- Class 1 lever, where the fulcrum is located among the enter pressure and the weight
- Class 2 lever, wherein the load is among the fulcrum and the input force
- Class 3 lever, in which the input force is between the fulcrum and the load
What is the function of a lever in technology?
Answer: A lever in generation is an easy device such as a rigid beam and a fulcrum. The attempt (enter force) and cargo (output force) are implemented at the opposite ends of the beam, with the fulcrum acting as the pivot point. When an attempt is carried out at one give-up of the lever, the load is moved at the opposite stop.
What is the concept of balance in terms of levers?
Answer: A lever stability is defined as a simple gadget that makes use of a rigid bar or beam to evaluate the weights or forces of two items. It determines if they’re in equilibrium (balanced) or if one side is heavier than the alternative (unbalanced). The fulcrum is the fixed factor around which the lever pivots to reap balance.
What is the classification of a lever?
Answer: 3 sorts need to be understood: – 1st magnificence levers have the fulcrum inside the center – second elegance levers have the burden within the center – third class levers have the attempt in the center. Each lever includes three components. Pro tip: The middle factor determines whether a lever is 1st, 2nd, or 3rd elegance!
What is the means of a lever in accounting?
Answer: Financial leverage is called after the physical lever, which amplifies a small enter force into a larger output force. Similarly, successful financial leverage amplifies small amounts of borrowed money into huge earnings.
What is the purpose of a manipulated lever?
Answer: A control lever or fitting is connected to the give-up of a manipulated cable and complements the applied pressure for activating a manipulated cable, adjusting tension, or multiplying the force brought through the cable.