What Is Powder Metallurgy?
Powder metallurgy is a time period that covers a huge variety of techniques used to provide substances and parts from metallic powders. This manner eliminates or considerably reduces the use of steel removal tactics, notably reducing production yield losses and frequently lowering prices.
Powder metallurgy is a metallic forming procedure wherein compressed metallic powder is heated to simply below its melting factor. This technique has been round for greater than a hundred years, however over the past zone century it has extensively established to be an great manner to supply exquisite components for a lot of vital applications.
This success is due, among other matters, to the benefits this technique gives compared to other forming strategies which include forging and steel casting, benefits in material use, complexity of form, and control of surrounding geometry. Network form. These in flip contribute to sustainability and make powder metallurgy identified as a green technology.
Powder Metallurgy Processes
These production strategies normally consist of all or maximum of the following technique steps:
• Production of steel powders
• Mixing and mixing
• Compression and shaping of powders
• Sintering of compacts to enhance integrity and energy
In a few instances, this process includes calibration, coining, infiltration, Used together with secondary operations together with warm forging.
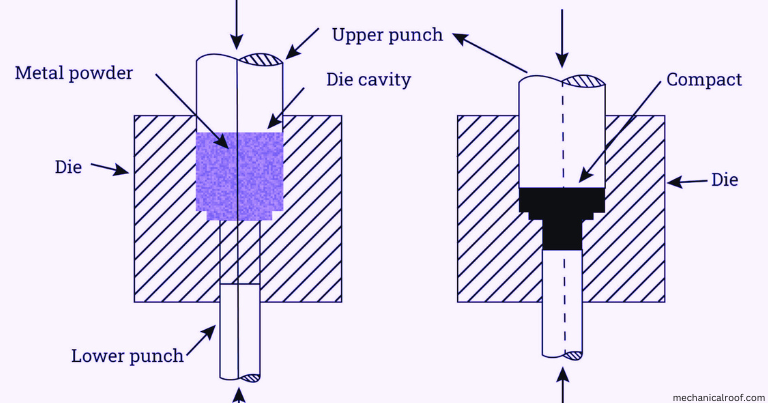
1. Powder Production
Almost all iron powders for PM aspect manufacturing are produced through the sponge iron technique or the water atomization approach. Nonferrous metallic powders used in other PM applications may be produced with the aid of a whole lot of strategies.
2. Powder Mixing
This frequently includes the incorporation of alloying additives in the form of elemental powders, or the incorporation of press lubricants.
3. Forming the combined powder into a compact
The fundamental consolidation system entails pressing a inflexible device set which includes a die, punch, and once in a while a mandrel or core bar. However, several different integration strategies are used in niche packages.
4. Sintering of compacts to enhance integrity and electricity
In this procedure step, the material is generally heated in a defensive surroundings to a temperature underneath the melting factor of the primary components.
In some cases, hint additives may shape a liquid phase on the sintering temperature. This case is known as liquid section sintering. The mechanisms concerned in sintering within the stable and liquid phases are briefly mentioned in later sections.
5. Secondary operations
Application of completing strategies to sintered elements. In powder metallurgy, such procedures are often referred to as “secondary operations.”
Advantages Of The Powder Metallurgy Process
- Minimizes machining by production components at or close to very last dimensions
- Minimizes scrap losses with the aid of usually the usage of greater than ninety seven% of the raw materials within the completed product
- Allows for quite a few alloy structures
- Produces desirable floor high-quality
- Provides the material may be warmth handled to enhance energy and put on resistance For self-lubrication or filtration
- It helps the creation of complex or particular shapes which are impractical or not possible with diverse metalworking methods.
- Suitable for medium to excessive-grade machining of components High extent
- Provides long-term overall performance reliability in critical applications
Related FAQ’S
What elements impact powder metallurgy?
The residences of powder metallurgy merchandise depend upon system parameters which includes compaction stress, sintering temperature, sintering time, kind and diploma of reinforcement, and length of the matrix and reinforcing elements.
What are the restrictions of powder metallurgy?
Although PM has blessings, powder metallurgy has the subsequent 3 risks. Limitations due to length and shape. It is pricey and useless in small doses. Density relies upon on compression ratio.
What is powder metallurgy excellent for?
Powder metallurgy (PM) is an established environmentally pleasant manufacturing technique for generating internet foam components. For the automotive industry, the opportunity of the usage of PM to permanently and value-efficiently mass produce dependable precision parts could be very attractive.
What first-class troubles can arise with powder steel components?
Fatigue is a completely complicated problem, however many powder-primarily based parts are prone to fatigue loading and provide sufficient fatigue energy to fulfill design requirements. The majority of component failures are due to fatigue, no matter whether or not the component is made with PM or a aggressive manner.
What is the temperature in powder metallurgy?
At higher sintering temperatures of 1350 °C, powder metallurgy bonds shape swiftly and crosslink. During the heating process at excessive temperature, the diffusion mechanism becomes active and the porosity decreases. The energy introduced to the powder particles contributes to the mass bonding of the powder.
How massive is the powder in powder metallurgy?
The average particle size required for metallic powders used in additive production methods is among 5 μm and one hundred fifty μm. This is determined by way of particle length analysis. G. Through dynamic photograph evaluation.
Why is powder metallurgy used for gears?
Powder metallic gears are extensively used in these industries because they may be synthetic again and again, uniformly, and inexpensively. It is also porous, which reduces weight, reduces noise, and might meet the unique needs of lots of programs.