Introduction
The engine is the coronary heart of a vehicle. It is a complex device that converts warmth from combustion gases into strength that drives the wheels. The chain of reactions that acquire this purpose is started out by using a spark that ignites a aggregate of gasoline and compressed air in a briefly sealed cylinder, causing it to burn rapidly.
As the aggregate burns, it expands, providing the electricity that powers the vehicle. Let’s take a more in-depth observe what an engine is and what sorts of engines there are.
What Is An Engine?
An engine is a machine that burns gas and converts it into mechanical power. Most modern automobiles use internal combustion engines that ignite the fuel and use the reaction to transport mechanical parts. Engines inclusive of the ones used to power motors can run on quite a few fuels, extensively fuel and diesel for vehicles.
However, there are also numerous varieties of opportunity fuels, together with biofuels and natural gas. In thermodynamics, engines, normally known as warmth engines, produce macroscopic motion from heat. The warmth in this case comes from the combustion of a gas inside the engine, which moves a piston.
Mechanical warmness engines convert heat into work thru various thermodynamic procedures. The internal combustion engine is possibly the great-regarded instance of a mechanical heat engine, in which the heat from the combustion of a gas rapidly pressurizes the gaseous combustion merchandise in a combustion chamber, which make bigger to drive a piston that rotates a crankshaft.
Unlike internal combustion engines, response engines produce thrust through ejecting a response mass in keeping with Newton’s 1/3 regulation of movement.
Besides warmness engines, electric motors convert electric energy into mechanical movement, pneumatic vehicles use compressed air, and wind-up motors in wind-up toys use elastic strength. In organic structures, molecular motors such as myosin in muscle groups use chemical power to generate force and in the end motion (chemical vehicles, however not warmth motors).
Chemical warmth engines that use air as a part of the fuel reaction are considered air-respiratory engines. B. Missiles, deep-sea submarines Engineers measure engines by the number of cylinders and the quantity of the cylinders. For instance, a 350 V8 is an engine with eight cylinders arranged in a V-shape and a displacement of 350 cubic inches.
In 2021, current automobile engines are high-quality understood while divided into three essential categories: These consist of:
• Internal Combustion Engine
• Hybrid Engine (Internal Combustion Engine + Electric Motor)
• Electric Motor
Now allow us to speak the specific sorts of engines one by one.
Types Of Engines
- External Combustion Engine
- Internal Combustion Engine
- Hybrid Engine
- Electric Engine
- Steam Engines
- Gas Turbine Engines
- Rocket Engines
- Stirling Engines
- Wankel Engines
- Pneumatic Engines
1- External Combustion Engine
An outside combustion engine (EC engine) separates gas and exhaust products. It burns the gas interior a chamber and heats the working fluid within the engine via a warmth exchanger or through the engine partitions. The steam engine, the father of the Industrial Revolution, falls into this class.
In a few respects, EC motors paintings further to their inner combustion engine counterparts: each require warmness, that’s generated via the combustion of a substance. However, there are some differences:
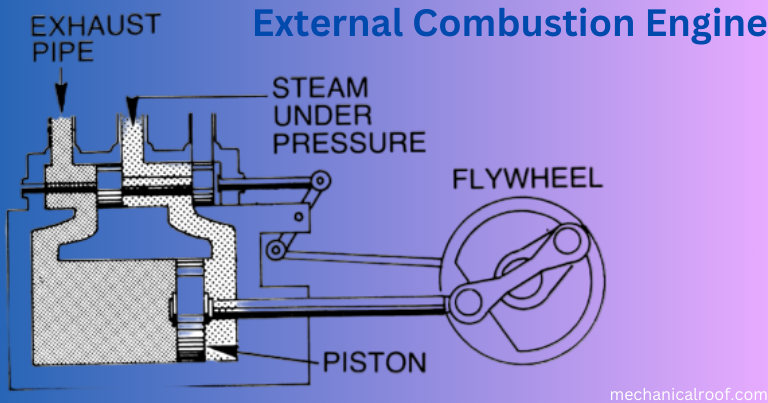
EC motors use a fluid whose chemical composition does not exchange when it undergoes thermal expansion (contraction) or phase shift. The liquid used may be either a gasoline (inside the case of a Stirling engine), a liquid (in engines with an organic Rankine cycle) or one which adjustments section (within the case of a steam engine). In an internal combustion engine, the liquid is most often a aggregate of: liquid gas and air that is burned (converting chemical composition).
Finally, the engine can both drain the fluid after use, as in the case of an inner combustion engine (open circuit engine), or use the identical fluid constantly (closed circuit engine).
2- Internal Combustion Engine
An inner combustion engine is an engine wherein the combustion of gasoline takes area in an enclosed area, the so-known as combustion chamber. The exothermic response of gasoline with oxidizer produces gases at high temperature and stress that could amplify.
The defining function of an internal combustion engine is that it does useful work by way of the direct movement of expanding hot gases to purpose movement, as an example with the aid of acting on a piston or rotor, or by means of pushing or shifting the whole engine.

Currently, two styles of internal combustion engines are synthetic: spark-ignited fuel engines and compression-ignited diesel engines. Most of them are 4-stroke engines. H. The work cycle is completed in four piston strokes. The strength cycle entails four awesome strategies: intake, compression, combustion and power cycle, and exhaust.
Spark-ignited fuel engines and compression-ignited diesel engines range within the way they supply and ignite the fuel. In a fuel engine, gas is blended with air and drawn into the cylinder for the duration of the consumption process.
The growth of the combustion gases pushes the piston ahead throughout the energy stroke. In a diesel engine, simplest air is drawn into the engine and compressed. A diesel engine then sprays a properly metered quantity of gas into the hot compressed air to make sure ignition.
3- Hybrid Engine
That’s easy. A hybrid combines at the least one electric powered motor and a gas engine to power the auto, and the system recovers electricity through regenerative braking. Sometimes the electrical motor does all of the paintings, from time to time the fuel engine does, and every now and then they work in tandem.
The end result is less gas consumption and consequently much less gas consumption. In a few cases, the more electrical power may even enhance overall performance.
All get their power from a high-voltage battery (separate from the car’s traditional 12-volt battery). This battery is replenished by way of soaking up electricity from deceleration. In conventional motors, this energy is normally lost thru warmness generated via braking. (This is achieved thru a regenerative braking machine.)
Hybrids also use the gas engine to fee and keep the battery. Automakers use a number of hybrid designs to accomplish extraordinary obligations, from maximizing fuel financial savings to retaining automobile charges to a minimal.
4- Electric Engine
Unlike common inner combustion engine automobiles that run on gas, electric vehicles do not require the explosive combustion of burnt gasoline to produce the electricity had to flow.
Instead, they use electrical electricity saved inside the battery to power electric powered motors linked to the wheels, which move the automobile forward. As a end result, electric powered automobiles have fewer moving elements than fuel-powered cars and normally require much less renovation, but currently have a better preliminary cost.
An electric powered motor is a device that makes use of electricity to generate mechanical power. They are commonly used to power a huge variety of programs, together with motors, trains, elevators, and family home equipment.
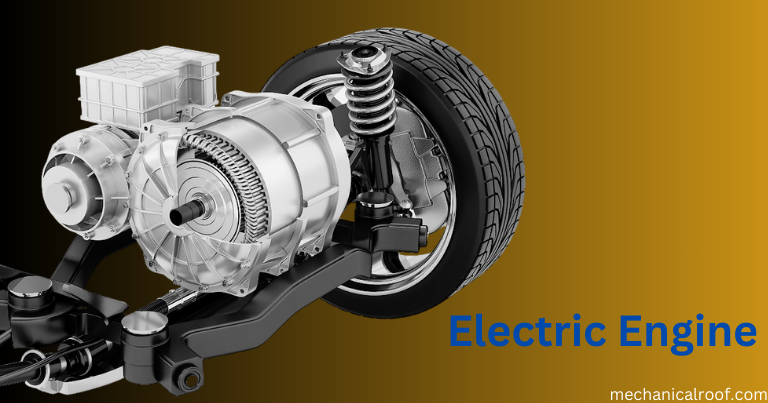
An electric powered motor works with a coil of cord, referred to as a rotor, placed in a magnetic discipline. When an electric powered cutting-edge flows thru the wire, it creates a magnetic area across the rotor. The interplay between the magnetic area of the rotor and the magnetic area of the stator (the desk bound thing of the motor) reasons the rotor to rotate and generates mechanical electricity.
There are unique sorts of electric powered motors, along with DC motors, AC cars, and stepper motors. DC automobiles use direct current (DC) to force the rotor, at the same time as AC automobiles use alternating modern (AC). Stepper cars are a form of electric motor that can be exactly controlled and are frequently used in programs that require precise motion, together with printers and robots.
5- Steam Engines
A steam engine is a device that makes use of steam to generate mechanical power. Once broadly used in trains, ships, and different programs, they may be now more often than not used to generate power in energy flora.
A steam engine heats water to produce steam, that’s then used to force a piston or turbine. Steam is produced by burning a gas along with coal or herbal gas in a boiler.
Heat from the combustion of the gas is used to warmth water, which in turn produces steam. The steam is then sent via valves into a cylinder or turbine, wherein it pushes a piston or rotor to produce electricity.
There are two fundamental forms of steam engines: piston engines and turbine engines. Reciprocating engines use pistons to transform steam stress into linear motion, even as turbine engines use rotors to transform the steam’s energy into rotational motion.
6- Gas Turbine Engines
A fuel turbine engine is an engine that makes use of the expansion of hot gases to generate energy. They are normally utilized in plane, electricity plant life, and other programs wherein a excessive electricity-to-weight ratio is needed.
Gas turbine engines work with the aid of compressing air, blending it with fuel, and burning it to produce warm gases. The hot gases enlarge through a turbine, turning a shaft and generating power. The power produced by way of the turbine is used to strength a compressor that forces greater air into the engine, or to power hundreds such as mills or plane propellers.
There are foremost types of gas turbine engines: simple-cycle gasoline turbines and blended-cycle gasoline mills. Simple-cycle gasoline turbine engines are the most effective type and use best one turbine to generate energy. They produce high energy however have low standard efficiency because electricity is misplaced inside the exhaust gases.
Combined-cycle gasoline turbine engines are greater complex and use two or extra thermodynamic cycles to generate energy. They typically consist of a fuel turbine, a steam turbine, and a waste warmness boiler (HRSG).
Gas generators generate energy with the aid of increasing hot gases produced through the combustion of fuel. Exhaust gases from the gasoline turbine are used to warmness water within the HRSG, generating steam. The steam is then extended thru a steam turbine to provide additional energy.
Combined-cycle gas turbine engines are greater efficient than easy-cycle fuel turbine engines due to the fact they can extract greater strength from the gasoline.
7- Rocket Engines
A rocket engine is an engine that makes use of the precept of motion and response to generate thrust to propel a automobile thru the air or space. They are utilized in rockets, missiles, and different spacecraft.
A rocket engine works by way of burning gas and oxidizer to provide warm gases that are expelled through a nozzle. The warm gases are released at high speeds, growing a pressure that pushes the rocket forward. This force is known as thrust.
There are numerous varieties of rocket engines, which includes stable rocket engines, liquid rocket engines, and hybrid rocket engines. Solid rocket engines use strong fuel and oxidizer, which are mixed and burned to supply thrust. They are easy and reliable, but can not be without problems switched off or controlled after ignition.
Liquid rocket engines use separate tanks to store the fuel and oxidizer, which are pumped into the engine and burned to supply thrust. These are more complicated and require extra maintenance, but may be without problems grew to become off and restarted, making them extra flexible and easier to govern.
Hybrid rocket engines use a combination of strong fuel and a liquid or gaseous oxidizer. They have a few benefits of each strong and liquid rocket engines, however are much less not unusual because of their lower overall performance and reliability.
8- Stirling Engines
A Stirling engine is an engine that makes use of a sealed cylinder of constant quantity to generate power. It can run on lots of fuels, together with sun strength, and is known for its high performance and occasional emissions.
A Stirling engine works by using the use of a working fluid, inclusive of air or hydrogen, that is heated and cooled inner a closed cylinder to produce strength. The operating fluid is heated by means of an outside warmth source, consisting of gas or sun power, and because it heats up, it expands.
The enlargement of the running medium pushes a piston or rotor, generating power. The working fluid then cools and contracts, and the system repeats.
Stirling engines are small and light-weight, so they are broadly utilized in small packages consisting of portable turbines and refrigeration devices. Due to their excessive performance and coffee emissions, they’re also used in massive scale packages such as energy plant life and ships.
9- Wankel Engines
Wankel engines are engines that hire a rotary design to convert fuel strength into motion. They are named after their inventor Felix Wankel and are recognized for his or her compact length and high electricity-to-weight ratio.
Wankel engines work with a triangular rotor that spins inside an elliptical chamber. The rotor is powered via the growth of a gasoline-air aggregate that pushes towards the edges of the chamber and spins the rotor. Spinning the rotor produces strength that can be used to energy masses which include automobiles and mills.
Wankel engines are commonly smaller and lighter than other types of engines, making them appropriate for use in small, portable programs. They also are quite easy and have few moving elements, making them clean to hold. However, they are now not as efficient as different kinds of engines and aren’t as generally used.
10- Pneumatic Engines
A pneumatic Engine is a motor that uses compressed air to generate power. They are typically used in business applications such as pneumatic equipment and control structures.
Air automobiles work by way of compressing air in a compressor and storing it in a tank. The compressed air is released through a valve and pushes a piston or rotor, producing strength. The electricity generated by using the air motor can be used to pressure masses together with gear and machines.
Air vehicles are known for his or her simplicity, low price and easy renovation. They also produce no dangerous emissions and are exceptionally safe to apply. However, they’re not as efficient as other sorts of engines and are restrained via the quantity of air they can save in a tank.
Different Types Of Internal Combustion Engines
The magnificence of the engines is based upon on the varieties of gasoline used, the paintings cycle, the huge variety of strokes, the kind of ignition, the extensive sort of cylinders, the association of the cylinders, the affiliation of the valves, the varieties of cooling, and so on.
These engines are utilized in severa areas such as the auto enterprise, plane enterprise, transport industry, and many others. Counting on their suitability in unique areas. So allow`s speak the specific engine kinds one with the aid of using one.
V Style Engines
V-engines, one of the maximum not unusualplace engine types, have their cylinders organized in a V-shape and constantly have a fair extensive style of cylinders – the same wide variety on each aspect of the V. These engines are typically prepared at a ninety-diploma angle and are typically determined in 6, eight, 10 or 12 cylinders. V Engines Pros and Cons:
- V-type engines typically boast of excellent engine displacement and a inflexible layout.
- They are steeply-priced to hold and complicated for humans to apprehend.
- Compact and lets in for extra cabin space.
- Ideal for large personal own family automobiles, vans, and unique vehicles in which more strength and towing capability are required.
- Examples of cars typically observed in our inventory segment with V-style engines encompass:
- Ford Expedition
- Honda Ridgeline
- Ford F-one hundred and fifty
- Honda Odyssey
Inline Engines
In-line (or “instantly”) engines have all the cylinders in a row, which means they have a propensity to be longer than the V configuration. For this reason, in-line engines are generally found in three-, 4-, 5- and six-cylinder versions, as 8 cylinders in a row might be too lengthy to suit in maximum engine cubicles.
BMW is well-known for its effective “line sixes” (in-line 6-cylinder engines). In-line four-cylinder engines have been notably famous in cutting-edge years because of their affordability, gas economy, and decreased emissions.
Some examples of exceptional, excellent used automobiles that have inline engines are:
- Mitsubishi Mirage
- Honda Accord
- Buick Regal
- Chevrolet Cruze
- Pros and Cons of an Inline Engine
- These engines are compact and light-weight.
- They are easy to restoration.
- They are instead sensitive engines.
- When attempting to find a used sedan, compact, or gas-green automobile, you need to assume to find out one with a four-cylinder inline engine. Their compact size, light-weight substances, and top gas overall performance cause them to best for powering smaller-sized passenger automobiles.
Flat Engines
Flat engines (additionally referred to as “boxer” engines) are arranged with the cylinders aligned horizontally so that after they hearth, they face each different (as if boxing every other). A boxer engine is basically a V-fashion engine where the V is opened to lie flat. Boxer engines are acknowledged for use in Porsches and some Subaru models.
Motorcycles, inclusive of those made with the aid of BMW in 2021, largely depend upon -cylinder flat engines.
- High-overall performance automobiles with flat engines have included the JaguarXK6,
- Pros and Cons of Flat Engines
- Vehicles with flat engines are properly-balanced and clean to handle.
- They may be massive engines and instead complex to understand.
Rotary Engines
A rotary engine is an inner combustion engine, like the engine for your vehicle, but it really works very in a different way from the traditional piston engine.
In a piston engine, the identical quantity of space (the cylinder) alternately plays four special tasks – intake, compression, combustion and exhaust. A rotary motor does the equal four jobs, but every happens in its own part of the case. It`s like having a separate cylinder for every of the 4 jobs, with the piston constantly shifting from one to the following.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wankel Engines
- These engines are smooth to apprehend.
- They are long lasting engines.
- In case of breakdown, it’s far very tough to find a certified mechanic.