Introduction
The carburetor is likewise referred to as the coronary heart of a vehicle, and if that heart” does now not characteristic properly, the engine can not be anticipated to feature properly, perform well, or run easily.
What Is A Carburetor?
A carburetor, additionally known as a carburetor, is a device for presenting an aggregate of gas and air to a fuel engine. Carburetor additives usually consist of a liquid fuel reservoir, a choke, an idle (or low-speed) jet, a main jet, a valve-like airflow restrictor, and an accelerator pump.
The carburetor adds fuel to the air to create a precisely acceptable aggregate for combustion inside the cylinder. Modern car cylinders are extra efficaciously powered by means of fuel injection systems that use much less fuel and pollute less.
However, carburetors are nonetheless utilized in small engines in garden mowers and chainsaws, as well as in older automobile and motorbike engines. The the gasoline engine is designed to draw in the proper quantity of air for proper gasoline combustion, whether or not the engine is started out bloodless or warm at top pace.
Ensuring the right mixture of gas and air is the activity of a smart mechanical tool called a carburetor. A carburetor is a tube that brings air and gasoline into the engine through valves and mixes them in different quantities to match special operating situations.
You would possibly assume the word “carburetor” is a rather peculiar phrase, however, it comes from the verb “carburetor”. This is a chemical time period meaning condensing a gas via combining it with carbon or hydrocarbons. So technically, a carburetor is a device that saturates air (fuel) with gasoline (hydrocarbons).
Types Of Carburetor
There are 3 varieties of carburetors:
- Up-draft carburetors
- Horizontal type carburetors
- Down-draft kind carburetors
1. Up-draft carburetors
An upflow carburetor is a type of carburetor, a component of the engine that mixes air and fuel, with air entering from the lowest and exiting from the pinnacle to reach the engine. The
updraft carburetor turned into the first not unusual type of carburetor. According to Edward Abdo in Power Equipment Engine Technology, with an updraft carburetor, air flows upward into the Venturi tube. Other types consist of downdraft and sidedraft carburetors. Upflow carburetors may additionally require a drip catcher.
2. Horizontal type carburetors
This carburetor operates with lower air velocities and large passages. This is because gravity helps the mixture circulate the cylinder.The downdraft carburetor can supply huge amounts of fuel for excessive pace and excessive performance while wanted. In this form of carburetor, air comes from the pinnacle of the mixing chamber and gas comes from the bottom of the combination chamber. The equal precept works here, the poor strain created by way of the 2 venturi tubes is exhausted through the tubes and mixes the gasoline and air.
3. Down-draft kind carburetors
This type of carburetor is used whilst set up space is confined. In a horizontal or facet-draft carburetor, because the name shows, the jet pipe is arranged horizontally. Another advantage of this kind of carburetor is that there may be no right perspective mechanism in the intake vicinity, which reduces drift resistance.
The precept of operation of this type of carburetor is quite simple. Here, the carburetor stays in a horizontal function and air flows in from one end of the carburetor, as proven inside the following determine. It is then mixed with gasoline to form an air-fuel combination, that’s then sent into the engine cylinder for combustion.
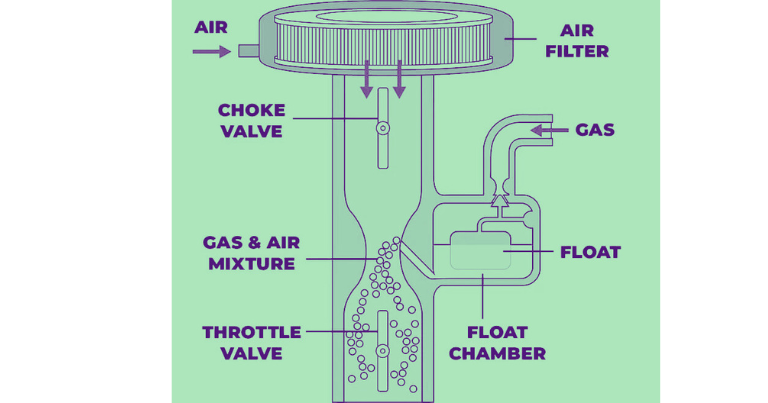
Parts Of Carburetor
Blow are the parts of carburetor:
- Throttle Valve
- Strainer
- Ventura
- Metering system
- Idling system
- Float Chamber
- Mixing Chamber
- Idle and Transfer port
- Choke Valve
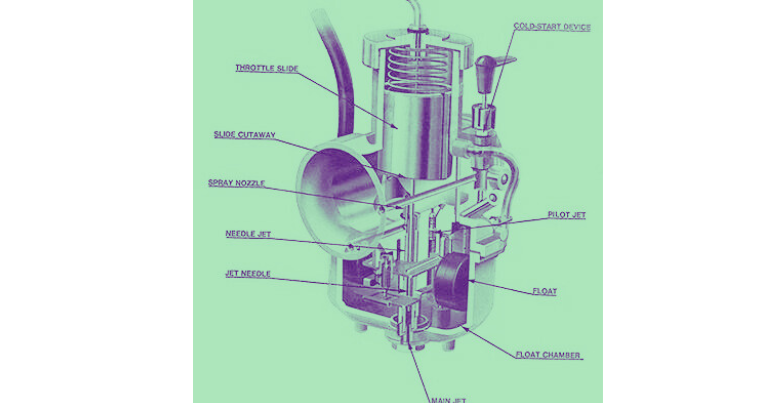
1. Throttle Valve
A valve that regulates the supply of liquid such as steam, gas, or air to the engine, and is robotically operated via a handle, lever, or specially a regulator.
2. Strainer
A tool used to clear out the gas earlier than it enters the drift chamber. It includes a best cord mesh that filters the gas and removes dirt and other airborne particles from the gas. If these particles are not eliminated, the nozzle may also grow to be clogged.
3. Ventura
Air flows thru a narrow throat within the carburetor referred to as a venturi, accelerating the air glide at that vicinity. The faster the air flows, the decrease the stress, developing a moderate vacuum inside the venturi. The gasoline jet flows into a venturi tube and a partial vacuum attracts the gasoline through the jet and into the air movement.
4. Metering system
The gasoline outlet nozzle is located inside the carburetor tube, with its open give up located at the throat or narrowest a part of the venturi tube. This stress differential or metering pressure causes gas to flow out of the outlet nozzle.
5. Idling system
Provides air-gasoline aggregate at a speed of approximately 800 rpm or much less than 20 miles consistent with hour. When the engine is idling, the throttle is nearly closed. Air flow thru the air horn is limited to create enough poor pressure within the venturi.
6. Float Chamber
A drift chamber is a tool for robotically regulating the fluid deliver to a gadget. It is maximum typically observed in internal combustion engine carburetors and automatically meters the quantity of fuel added to the engine.
7. Mixing Chamber
The mixing chamber contained a combination of air and gasoline. It is then supplied to the engine cylinder.
8. Idle and Transfer port
In addition to the main jet in the venturi part of the carburetor, two additional jets or ports deliver gas to the engine cylinders.
9. Choke Valve
A choke valve may be hooked up inside the carburetor of an internal combustion engine. Its purpose is to throttle the airflow and enhance the combination when the engine starts offevolved.
How Does A Carburetor Work?
The carburetor uses the vacuum created by way of the engine to draw air and gasoline into the cylinder. The throttle valve can be opened or closed to permit greater or much less air into the engine. This air flows thru a slim beginning called a venturi. This creates the negative strain that had to maintain the engine walking.
Carburetors vary widely in design and complexity. The simplest choice is largely a large vertical air pipe established above the engine cylinder and a horizontal gas pipe connected to one aspect of it.
When air flows via a tube, it has to pass through a slim bend within the center, increasing its speed and decreasing its pressure.
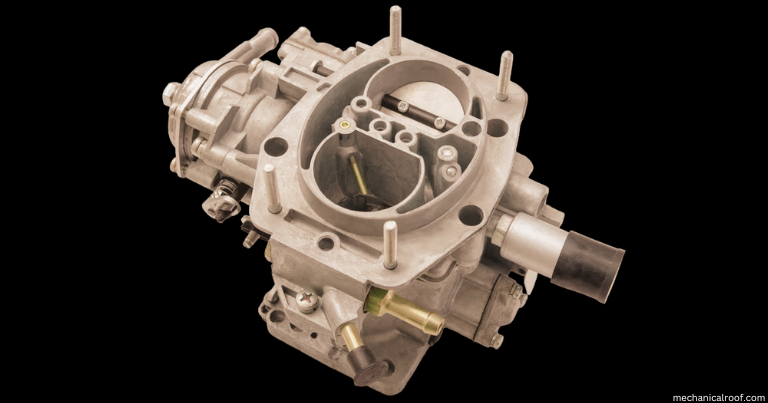
This twisted component is known as a venturi. The drop in air pressure creates a suction effect that draws air from the side gasoline traces.
When a fluid enters a narrow space, its speed will increase but its strain decreases. This explains why the wind whistles among buildings, and why canal boats floating parallel to every other are frequently jostled.
Here’s how Carburetor works:
- Air flows through the car’s air intake on the top of the carburetor and passes through a filter to take away particles.
- When the engine is first commenced, the choke may be adjusted to nearly block the pinnacle of the pipe to lessen the quantity of air coming in (this will increase the gasoline content of the combination entering the cylinder). Masu).
- In the center of the tube, the air passes through a narrow bend called a venturi. This increases velocity and decreases strain.
- The drop in air pressure creates a suction pressure in the gasoline line, sucking in fuel.
- A restrictor is a valve that rotates to open and close a pipe. When the throttle is opened, extra air and gasoline circulate the cylinders, permitting the engine to supply greater energy and the car to go quicker.
- The aggregate flows downward into the cylinder.
- Fuel is provided from a mini gas tank called a float bowl.
- When the gas level drops, the flow inside the chamber lowers and the valve at the top opens.
- When the valve opens, more fuel flows from the primary gasoline tank to fill the chamber. This reasons the drift to upward thrust and near the valve once more.
Functions Of Carburetors
The most important functions of a carburetor are:
- The most important characteristic of a carburetor is to mix air and petrol and offer a distinctly flamable mixture
- To manage the engine speed
- It additionally regulates the air-gas ratio
- To increase or lower the quantity of aggregate because the engine speed and cargo alternate
- To hold constant gasoline strain within the flow chamber.
- The gas evaporates and mixes with air to form a homogeneous mixture.
- To offer the proper quantity of air and gas combination at the right electricity below all engine load and speed conditions.
Applications Carburetor
- Used in spark ignition engines.
- Used for automobile speed control.
- Converts the main gas, gasoline, into great droplets that mix with air and burn without problems and uniformly.
Carburetor Advantages:
- Carburetor components aren’t as highly-priced as injectors.
- Using a carburetor affords greater air and gasoline combination.
- Carburetors display greater electricity and precision in road tests.
- Because the carburetor isn’t restricted by way of the quantity of gas pumped out of the fuel tank, the cylinder can draw greater gasoline through the carburetor, ensuing in a denser mixture in the chamber and big power. .
Carburetor Disadvantages
- At very low speeds, the combination furnished by using the carburetor is so susceptible that it does now not ignite properly and under such conditions some provision is required within the carburetor to reinforce the aggregate .
- Carburetor operation is stricken by changes in atmospheric stress.
- A carburetor is heavier than a fuel injector and consequently consumes greater gasoline.
- Higher atmospheric emissions than injectors.
- Carburetor upkeep costs are higher than gasoline injection device preservation costs.
How do you clean the carburetor?
Check the instruction manual before cleaning the carburetor. Always follow the manufacturer’s complete commands for cleaning and maintenance. Make sure the carburetor is cool to the touch earlier than cleansing.
1. Dilute the cleanser: Mix the diluted cleaner in a large container. However, it is important to use a non-corrosive cleaner that will not assault or smash the carburetor’s plastic or rubber parts. Avoid the use of vinegar, as acetic acid makes metallic more at risk of rust. Also, never use bleach, as sodium hypochlorite (bleach) corrodes metals together with metal and aluminum, and corrodes rubberized seals.
2. Clean the air filter out: Before cleansing the carburetor, test the air filter out to ensure that the air coming into the carburetor is clean and freed from blockages that could cause black smoke to be emitted from the exhaust. Please. Shut off the gas supply and do away with the spark plug wires if prepared. Remove the housing and wing nuts securing the clear out and take away the outer element.
3. Remove the carburetor: If essential, use pliers and a screwdriver to take away cowl plates, shields, linkages, and hoses. Also, take away any covers or clamps conserving the carburetor in the region and dispose of the hose clamps connecting the carburetor to the gasoline traces. Remove the carburetor and use compressed air to blow any extra particles out of the outer casing. (Note: If you’re unexpected with this process, consult a professional earlier than cleansing.)
4. Remove the Carburetor Float: Remove the screw that secures the carburetor waft (a cup-like container). Be careful now not to permit any leftover fuel to get into the carburetor (and get rid of it safely). This is a commonplace motive of paint buildup inside the carburetor. Also, remove the pin that rotates the drift and keep it in a secure vicinity. Then pull the float directly out of the housing.
5. Remove different detachable additives: Note the area and association of other carburetor components to be removed so they’re on hand for cleaning.
6. Soak and Scrub the Components: Soak the carburetor drift and different additives in a large box with diluted cleanser and permit it to soak absolutely for 10 minutes. Use a brass brush to clean all metal elements and a stiff nylon brush to wash plastic components. Make sure the small vents are wiped clean. Wash small elements with a cleaning solution.
7. Rinse and Dry: Rinse all components of the carburetor in a bucket of smooth water and allow to air dry absolutely. For small holes or vents, use a can of compressed air to eliminate excess moisture.
8. Reassembly and Replacement: Carefully reassemble the carburetor and install it on the engine. Reconnect all hoses, clamps, and wires.
Related FAQ’S
What does a carburetor do?
Answer: The process of a carburetor is to deliver an air-gas combination to an inner combustion engine. The carburetor regulates the glide of air through a prime bore (the venturi), which in turn sucks in the gas, and the combination enters the engine thru the intake valve.
Why did carburetors fall out of use?
Answer: Fuel injection systems subsequently changed carburetors because they may be better controlled, resulting in more green gasoline use, less pollution, and decreased gasoline intake. After 1970, power and overall performance were the primary motives fuel injection systems changed carburetors.
How do I recognize if my carburetor is faulty?
Answer: Here are four signs that your carburetor desires to restore.
1. Does no longer start.
2. The operation is efficient.
3. Things are going well.
4. It’s flooded.
Can a car run with an awful carburetor?
Answer: Therefore, if trouble occurs, it could loosen the combination and affect the engine’s overall performance. A terrible carburetor can cause your engine to accelerate slowly, notably decreasing overall performance and fuel consumption.
Do carburetors use greater gas?
Answer: A carburetor that passes extra air does no longer necessarily use more gasoline. In reality, for the equal engine, a carburetor with a higher CFM score often calls for a bigger gas jet than a smaller carburetor to attain the identical air-gas ratio.
What is the carburetor linked to?
Answer: The carburetor is attached to a throttle cable attached to the gasoline pedal. When you press the accelerator, the carburetor literally opens to suck in extra air, and even greater gasoline, extracting more strength and speed out of your engine.
What’s inside the carburetor?
Answer: There is a component referred to as a nozzle in the carburetor. This is an opening that lets in gas from the flow bowl to mix with air earlier than coming into the engine’s cylinders. The drift chamber holds a small quantity of fuel within it and permits gas to flow to the nozzle as needed.
What is the carburetor manufactured from?
Answer: The principal structure and largest a part of the carburetor is a molded body manufacturers from lightweight alloy and aluminum. There is little strain or strain on a stationary body, so there is no want for more potent metals. The transferring elements of a carburetor are made of metallic or chrome steel.
Do all motors have carburetors?
Answer: Carburetors are no longer used on new automobiles. However, they are still used in many older automobiles and are at risk of problems including clogged jets and worn or broken components. Regular maintenance and inspection will assist hold your car’s carburetor in exact condition.