Introduction
Today, we can be shifting in the direction of electric powered and opportunity gas cars, but allow’s not forget that each one the magic started out with the internal combustion engine. the engine is the heart of the automobile. A automobile engine is a complicated machine made up of diverse parts that paintings together to energy the car.
Knowing the special components of the engine and their functions can without difficulty identify the part that is causing the hassle and take appropriate measures. Moreover, know-how the elements of a automobile engine allow you to make an knowledgeable choice when shopping for a vehicle or whilst making an improve or modification.
Here is a listing of the exclusive components of a vehicle engine and a few hints to increase their lifespan.
Basic Of Car Engine
A car engine is a complex mechanism with several inner components running like clockwork to power your automobile. For an engine to characteristic properly, all of its parts ought to be in proper situation.
The engine is the coronary heart of your car. It is a complicated system that converts warmth from the combustion gases into energy that drives the wheels.
It consists of two basic parts. The lower, heavy segment is the cylinder block, that’s the housing for the engine’s maximum vital shifting elements. The removable top cowl is the cylinder head.
To face up to high hundreds, an engine must be of robust creation. An engine is started by means of a spark, which ignites a combination of gas vapor and compressed air in a briefly sealed cylinder, inflicting it to burn swiftly.
That is why this gadget is also referred to as an internal combustion engine. As it burns, the mixture expands, generating energy to force the car.
The cylinder head contains valve-managed channels thru which the air-fuel combination enters the cylinder, and other channels through which the gases produced during combustion go out.
The block houses the crankshaft, converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion at the crankshaft. Often the block also homes a camshaft, which operates the mechanism that opens and closes the valves within the cylinder head.
Now permit’s have a look at all the parts that work together to make this viable.
Car Engine Parts Diagram With Name
The diagrams under display engine elements by means of location.
List Of Car Engine Parts Names
- Engine block
- Piston
- Cylinder Head
- Crank Shaft
- Camshaft
- Timing belt
- Engine Valves
- Oil Pan
- Combustion chamber
- Intake manifold
- Exhaust manifold
- Intake and Exhaust valves
- Spark Plugs
- Connecting Rod
- Piston Ring
- Gudgeon pin
- Cam
- Flywheels
- Head gasket
- Cylinder Liner
- Crank Case
- Distributor
- Distributor o ring
- Cylinder headcover
- Rubber grommet
- Camshaft pulley
- Oil filter
- Water pump
- Timing belt drive pulley
- Oil pan drain bolt
- Turbocharger and supercharger
- Starter motor
Parts Of An Engine
An car engine consists of the engine block (cylinder block), combustion chambers, cylinder head, pistons, crankshaft, camshafts, timing chain, valves, rocker palms, pushrods/lifters, injectors, spark plugs, oil pan, distributor, connecting rods, piston earrings, and flywheel.
1. Engine Block
The engine block is the principle a part of the engine. It is regularly made of aluminum or iron and has numerous holes that house the cylinders. It additionally serves as a passageway for water and oil to cool and lubricate the engine. The oil passages are narrower than the water passages.
The engine block houses the pistons, crankshaft, camshafts, and, relying at the vehicle, has 4 to twelve cylinders arranged in a row, additionally referred to as in-line, flat, or V-fashioned.
All different elements of the engine are essentially bolted collectively. The interior of the block is where the magic happens, together with combustion.
2.Pistons

Pistons are the moving parts of the engine that take a seat in the cylinders and are made hermetic via piston jewelry. They are cylindrical with flat surfaces to compress the air-fuel combination. The
pistons are responsible for transferring the energy produced in the combustion cycle to the crankshaft that powers the car.
Pistons pass up and down in the cylinder two times for every revolution of the crankshaft. This is why the pistons in a 1250 RPM engine move up and down 2500 instances in step with minute.
Inside the piston are the piston jewelry, which make contributions to compression and decrease friction resulting from the constant friction of the cylinder, the compression rings and the oil jewelry, which seal the combustion chamber and save you oil from coming into this place.
Pistons are usually made from aluminum alloys, which are lightweight and have correct thermal conductivity. It should be precisely machined to match the cylinder bore and allow the engine to run nicely. A vehicle engine’s
piston hurries up from zero to over 53 miles per hour (85 km/h) over a distance of three inches (7.62 cm), then back to zero again.
3.Cylinder Head
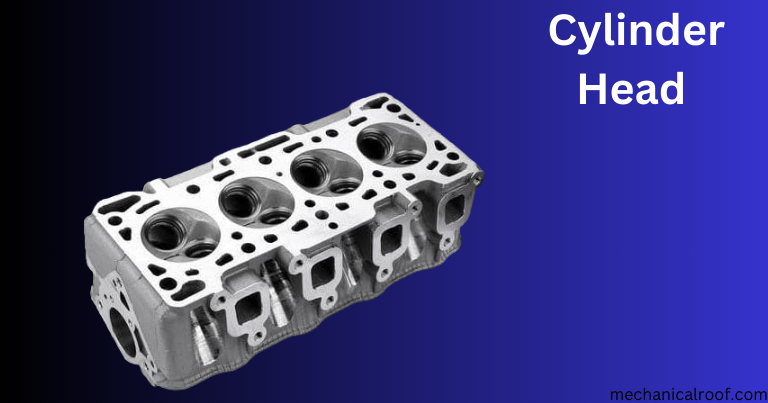
It is hooked up to the engine by using a cylinder screw and sealed by means of a head gasket.
The cylinder head contains many components consisting of valve springs, valves, lifters, bumpers, rocker fingers, and camshafts to manipulate the passageway that permits consumption air to flow into the cylinder all through the consumption stroke.
4.Crankshaft
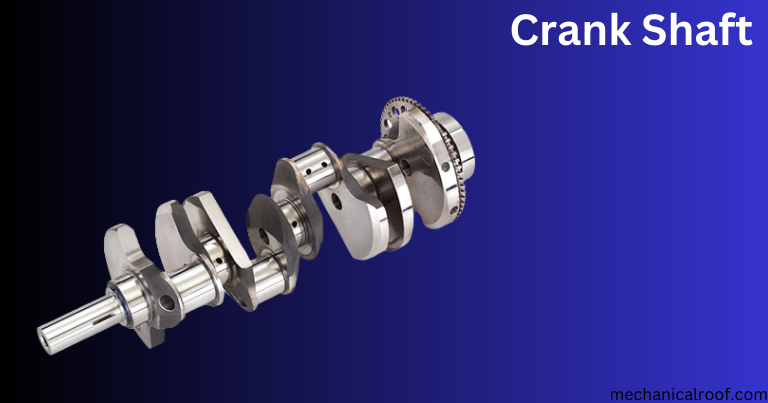

The crankshaft is positioned at the lowest of the engine block, inside the crankshaft journal (the region of the shaft that rests at the bearings).
This carefully machined and balanced mechanism is attached to the pistons via connecting rods.
Like a field devil, the crankshaft converts the up and down movement of the pistons into from side to side motion at engine speeds.
5. Camshaft
Depending on the vehicle, the camshaft is located both in the engine block or in the cylinder head.
Many modern cars have a dual overhead camshaft (DOHC) or additionally known as a single overhead camshaft (SOHC) within the cylinder head, supported with the aid of a hard and fast of oil-lubricated bearings for longer lifestyles.
The role of the camshaft is to time the opening and closing of the valves, receiving the rotary movement from the crankshaft and changing it into up and down motion to govern the movement of the lifters, remaining pushrods, rockers, fingers and valves.
6.Timing Belt/Chain
Automotive engine with a timing belt.
A timing belt, timing chain, or cam belt is the part of an engine that synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft in order that the engine’s valves open and near at the suitable time all through the intake and exhaust strokes of every cylinder.
In interference engines, the timing belt or chain is likewise crucial to prevent the pistons from hitting the valves. Timing belts are commonly timing belts, or force belts with enamel on the inner. Timing chains are curler chains.
Belts are made of durable rubber and feature gears that grip the camshaft and crankshaft pulleys. The chain is wrapped around a toothed pulley, similar to a bicycle chain.
7.Engine Valves
Engine valves are mechanical parts utilized in engines to modify the go with the flow of air, fuel, and exhaust gases in the combustion chamber or cylinder head at the same time as the engine is jogging.
The function of a valve is very simple: a cam pushes the valve into the cylinder towards a spring, establishing the valve to allow gases to drift, and then the spring forces the valve to close once more.
The pressure inside the combustion chamber could be very powerful at maintaining the valve closed.
8.OIL PAN
The oil pan is a simple however essential a part of the engine’s lubrication system. Oil circulates via each a part of the engine, keeping it lubricated. This reduces friction so the whole thing runs smoother. Without oil, friction might quickly smash the engine.
The oil pan keeps the oil contained in the lubrication gadget from leaking out. A gasket is placed between the oil pan and the engine mountings to permit metal-to-metal touch.
9. Combustion Chamber
The combustion chamber is the region inside the cylinder wherein the fuel and air combination is ignited. When the piston compresses the gasoline and air aggregate and it comes into contact with the spark plug, the mixture burns and is forced out of the combustion chamber within the shape of strength.
The cylinder homes the various vital components of an inner combustion engine, which include the fuel injector, piston, spark plug, and combustion chamber.
10. Intake Manifold
A vehicle’s consumption manifold is the a part of the engine that distributes airflow among the cylinders. It regularly contains the throttle plate (throttle body) and numerous different additives.
On some V6 and V8 engines, the intake manifold may also encompass several separate sections or parts.
Intake air flows thru the air purifier, intake manifold (snorkel), throttle body, into the intake manifold plenum, after which thru the runners to the cylinders. The throttle valve (throttle body) regulates the airflow, thereby controlling engine pace.
11. Exhaust Manifold
An exhaust manifold is often a simple cast iron or stainless-steel unit that collects engine exhaust gases from more than one cylinders and directs them to the exhaust pipe. It is connected to the exhaust valves. Its construction is similar to that of an intake manifold.
Exhaust manifolds have the same function in petrol and diesel engines, transporting exhaust gases in both instances.
12. Intake and Exhaust Valves
The intake and exhaust valves are used to control and regulate respectively the price (or air) being provided to the engine for combustion and the exhaust gases leaving the cylinder.
They are set up in the cylinder head or cylinder wall. They typically have a mushroom shaped head.
In a fuel engine, the air-gasoline aggregate enters thru the intake valve. But in diesel engine best air passes thru the consumption valve. In both cases the exhaust valve is to permit the exhaust gases to escape.
Consumption valves are related to the intake manifold and exhaust valves are connected to the exhaust manifold. Both consumption and exhaust manifolds had been explained above.
13. Spark Plug
A spark plug is a device that transmits electric modern from the ignition system to the combustion chamber of a gas engine, igniting the compressed gas-air combination by an electric powered spark whilst keeping the combustion pressure within the engine.
A spark plug has a metallic threaded housing that is electrically insulated from a middle electrode by means of a ceramic insulator.
The middle electrode may additionally comprise a resistor and is connected to the output terminal of the ignition coil or magneto through a closely insulated cable.
14. Connecting Rod
The connecting rod, together with the crank, converts the reciprocating movement of the piston into the rotary movement of the crankshaft.
Connecting rods are important to transmit the compressive and tensile forces from the pistons. In their maximum common shape, they permit pivoting movement at the piston stop and rotation at the shaft end in an internal combustion engine.
The predecessor of the connecting rod is the mechanical connection utilized in water generators to convert their rotary movement into reciprocating movement.
15. Piston Rings
A piston ring is a split metallic ring that fits around the out of doors diameter of the piston in an internal combustion or steam engine.
The fundamental functions of piston earrings in an engine are:
• To seal the combustion chamber so that as little gas as viable escapes into the crankcase.
• To improve warmth switch from the piston to the cylinder wall.
• To hold an appropriate amount of oil among the piston and cylinder wall.
16. Piston Pins
Piston pins, also referred to as wrist pins, are an essential part of an internal combustion engine.
They create the relationship among the connecting rod and the piston. Piston pins also can be utilized in connecting rods, wheels, and cranks.
17. Cam
It is an critical part of the camshaft. It is referred to as the camshaft because of the cam. The cam is connected to the camshaft and controls the consumption and exhaust valve timing.
Now allow’s speak approximately the most important a part of a car engine.
18. Flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical tool that shops rotational power using the conservation of angular momentum. It is a sort of kinetic electricity this is proportional to the fabricated from the moment of inertia and the square of the rotational velocity.
The torque furnished by using a motor is not uniform and evidently fluctuates. If the vehicle continues to transport with such fluctuations in overall performance, no longer best will it’s very unpleasant for the driver, but it’s going to additionally shorten the existence of every thing.
To resolve the problem of load fluctuations, a flywheel is used. Flywheel is usually connected to the camshaft. It shops torque when the value is high inside the operating cycle and releases torque whilst the fee is low. It acts as a torque buffer.
19. Gasket
A gasket is a hoop or plate of bendy fabric used in static applications to seal joints, flanges, and other mating surfaces to save you leakage.
These are the specific types of gaskets typically utilized in engines:
Exhaust Manifold Gasket. The exhaust manifold gasket is a multi-layer gasket that includes metal and other materials that provide the great seal viable. This is the first seal within the exhaust gadget and could be very critical to save you leaks.
Water Pump Seal. The water pump seal is a ring-formed part made from long lasting cloth that could face up to loads of temperatures. Located among the water pump and the engine block, it prevents coolant from leaking on its manner from the pump to the engine and again.
Oil Pan Gasket. The oil pan gasket is located among the oil pan and the bottom of the engine block, preventing oil from leaking on its way from the pan to the engine and lower back. Oil is constantly flowing, so if the seals are worn or no longer hooked up nicely, oil leaks can arise.
Related Products:
20. Cylinder Liner
Cylinder liners are thin cylindrical metal parts which can be connected to the engine block to form the cylinder. They are one of the most important useful elements inside the engine.
Cylinder liners act because the inner wall of the cylinder, maintain the lubricating oil inner and form the sliding floor for the piston jewelry.
21. Engine Distributor
A distributor is an enclosed rotating shaft used on spark ignition and automatically controlled ignition inner combustion engines.
The number one feature of a distributor is to send secondary or high voltage electricity from the ignition coils to the spark plugs in the best firing series and for the best period of time.
Except for magneto ignition structures and plenty of modern computer controlled engines that use crank attitude/role sensors, the distributor also consists of a mechanical or inductive breaker switch to open and close the ignition coil number one circuit.
22. Distributor O-Ring
Distributors typically use a unique size O-ring that fits over the distributor shaft and seals it to the engine – the so-called distributor O-ring.
The distributor O-ring definitely seals the distributor housing from the engine, stopping oil leakage at the bottom of the distributor. If the O-ring fails, oil leakage can occur at the bottom of the manifold, causing similarly problems.
23. Cylinder Head Cover
On many present day 4-stroke engines, the cylinder head cover houses the upper working factors of the engine manage unit, in addition to the crankcase air flow valves and all their peripherals.
It also protects the engine from dirt and different foreign items.
24. Rubber Grommets
Rubber grommets are used to shield or cowl holes and decrease vibration. Inserting a rubber grommet avoids sharp edges and protects the engine valves as they bypass thru the holes. The rubber grommets guard the valves from damage.
25. Camshaft Pulley
The camshaft pulley is a part of the engine’s timing device and is used to control the rotational speed of the camshaft. This component controls the poppet valves which are chargeable for providing and arduous air inside the cylinders.
The camshaft pulley is hooked up to a timing chain, which rotates the camshaft in sync with the crankshaft.
26. Oil Filter
A vehicle’s oil filter out also gets rid of waste materials. It traps dangerous deposits, dirt, and steel debris in the engine oil, keeping your vehicle’s engine walking smoothly.
Without an oil filter out, harmful debris can get into your engine oil and reason damage on your engine. Filtering out this junk maintains your engine oil cleanser and lasts longer.
27. Timing Belt Pulley
A timing belt pulley is a specialised pulley gadget with tooth or wallet alongside the out of doors of the diameter of the pulley body.
The outer tooth or wallet of the pulley aren’t used to transmit strength; instead, they engage the pulley belt to assist with timing and save you misalignment.
29. Water Pump
A car’s water pump is a belt-pushed pump that attracts its power from the engine’s crankshaft. Designed as a centrifuge, water pumps draw cooled liquid from the radiator through a valuable inlet inside the pump.
The fluid is then sent externally to the engine and back to the automobile’s cooling gadget.