Introduction
This blog will take an in-depth look at Gate Valve. The blog will bring more detail on topics such as:
- What Is A Gate Valve?
- Types Of Gate Valves
- Uses Of Gate Valve
- Working Of Gate Valve
- Gate Valve Construction
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of Gate Valve
- Related FAQS
- And Much More…
What Is A Gate Valve?
A sluice valve, also referred to as a gate valve, is a type of valve that functions by lifting a barrier (gate) away from the flow of the fluid. Gate valves take in the minimum area alongside the pipe axis and have a minimal effect on fluid going with the flow whilst completely open. The gate faces may be parallel, however they are usually wedge-shaped to exert pressure on the sealing floor.
The beginning and closing of a gate valve manage the drift of media. Its important function is its unobstructed immediately-through passageway, which results in minimal stress loss throughout the valve. Unlike butterfly valves, a gate valve’s unobstructed bore permits the passage of pigs during pipe cleaning techniques. These valves are available in a whole lot of sizes, substances, temperature and strain rankings, and gate and bonnet designs.
Gate valves are generally less costly than ball valves of the same size and pleasant. However, they have a slower actuation time in comparison to sector-turn valves and are pleasantly suited for programs where valve operation is rare, together with in-isolation valves. It is critical to observe that gate valves ought to most effectively be utilized in fully open or fully closed positions and are not designed to modify waft. While automated gate valves with electric or pneumatic actuators are to be had, manual gate valves are a greater price-powerful choice due to the fact they have confined usage.
Types Of Gate Valves
There are 3 types of Gate valves:
- Solid wedge gate valve.
- Flexible wedge gate valve.
- Split wedge or Parallel disks Valve.
1- Solid Wedge Gate Valve
The solid wedge is an extensively used and simple disk kind that is recognized for its strength. It is flexible and can be installed in any function, making it suitable for several fluids, together with turbulent float. However, one downside is that it can not compensate for changes in seat alignment because of pipe hundreds or thermal enlargement, making it prone to leakage. In high-temperature packages, the solid wedge may also revel in thermal locking, where the wedge becomes stuck between the seats due to steel growth. Due to those obstacles, stable-wedge gate valves are normally used in slight to lower stress-temperature conditions.

2- Flexible Wedge Gate Valve
The solid disk of the flexible wedge is manufactured from one piece and has a perimeter cut of various sizes, shapes, and depths. A smaller, narrower reduction on the perimeter gives much less flexibility but keeps strength, while a recessed or wider reduction offers greater flexibility but compromises strength. This layout complements seat alignment and guarantees better leak-evidence overall performance.
It is in particular powerful in conditions wherein thermal binding might also occur. Gate valves with flexible wedges are normally utilized in steam systems, where thermal enlargement can distort within the valve bodies, main to thermal blinding.
The flexibility of the gate allows it to bend as the valve seat compresses due to thermal expansion, stopping thermal blinding. However, a disadvantage of this layout is that fluid from the pipeline may additionally acquire in the disk, doubtlessly causing corrosion and weakening the disk over time.

3- Split wedge or Parallel disks Valve
The dual stable components of the Split Wedge Disk are held together by using a specialized mechanism. If one part of the disk becomes misaligned, the disk has the capability to adjust itself to the surface it’s miles seated on. The cut-up disk comes in bureaucracy: a wedge form or parallel disk. The parallel disks are equipped with springs that make certain consistent touch with the seats, taking into consideration bi-directional sealing.
The breakup wedge is especially beneficial for coping with noncondensing fluids and gases at both ordinary and elevated temperatures. The disk’s capacity to move freely prevents thermal binding, although the valve has been closed at the same time as the line is cold. This gets rid of the possibility of thermal blinding while the road is heated and expands because of the fluid.

Uses Of Gate Valve
A gate valve’s fundamental characteristic is to either completely block fluid waft or permit it to waft freely through a pipeline whilst completely open. This method it is only used within the fully closed or absolutely open positions. Unlike different valves, gate valves are not designed for waft law, however rather to close off the float of liquids.
When fully open, the gate valve creates minimum resistance within the flow route due to the absence of obstructions. The size of the open waft course isn’t always linearly related to the motion of the gate, ensuing in an uneven exchange in waft price as the stem is became. In a few cases, a partially open gate may also enjoy vibration from the fluid glide.
Gate valves are generally utilized in larger pipe diameters, ranging from 2′ to the most important pipelines, as they’re easier to construct compared to other styles of valves in large sizes.
Working Of Gate Valve
The number one components of a gate valve consist of the handwheel, spindle, gasket, bonnet, valve body, flange, and gate. The major mechanism of operation is simple: turning the handwheel reasons the stem to rotate, which in turn actions the gate up or down through the threads. To fully open or close the valve, it normally requires multiple rotations of the handwheel. By lifting the gate out of the go-with-the-flow course, the valve opens, and lowering it go into reverse creates a seal that closes the valve completely.
The glide charge in a gate valve is tormented by the gate’s vertical motion, with the maximum substantial modifications going on near the point of the entire closure. However, while used to alter float, the high velocity of the go with the flow at partial commencing can reason put on at the gate and seat. This, mixed with potential vibrations of the gate, can shorten the valve’s lifespan.
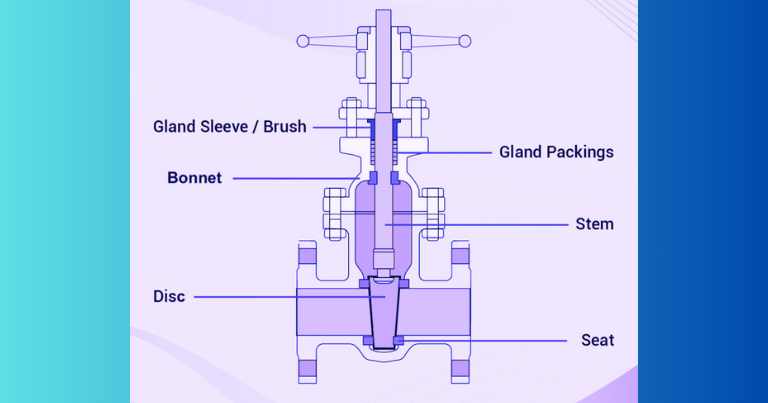
Gate Valve Construction
Gate valves are operated via a threaded stem that connects the actuator (which includes a handwheel or motor) to the gate. Their distinguishing feature is the vicinity of the threading on the stem, which can be either growing or non-growing. In growing stem valves, the stem is attached to the gate and acts up and down in tandem with the valve, imparting a visible indication of its role.
The actuator is hooked up to a nut that rotates around the threaded stem to control its movement. Non-growing stem valves, alternatively, have the stem constant to and rotating with the actuator, with the threading going into the gate. These valves might also have a pointer connected to the stem for position indication because the gate’s motion is hid interior.
Non-growing stem valves are desired in situations in which the vertical area is confined. Gate valves will have flanged ends that conform to pipeline-well-suited flange dimensional requirements. They may be comprised of a number of materials, such as forged iron, solid carbon steel, ductile iron, gunmetal, chrome steel, alloy steel, and cast steel.
All-metal gate valves are suitable for use in extremely excessive vacuum chambers to isolate exclusive sections of the chamber.
Bonnet:
Valve our bodies are sealed by bonnets, which can be screw-in, union, or bolted for gate valves. Screw-in bonnets are the only and provide a dependable, strain-tight seal. Union bonnets are ideal for common inspection and cleansing and also provide delivered electricity to the frame. Bolted bonnets are used for large valves and excessive-pressure programs.
Pressure Seal Bonnet:
In high-pressure gate valves, a pressure seal bonnet is frequently used. This sort of construction is appropriate for valves that perform at pressures above 2250 psi (15 MPa). The particular layout of the stress seal bonnet functions a downward-going through cup that suits in the valve body. As the internal pressure will increase, the edges of the cup are pushed outward, developing a better seal between the frame and the bonnet. This isn’t the same as other constructions where the seal is created via outside clamping pressure, that could cause leaks inside the body-bonnet joint.
Knife Gate Valve:
For substances including plastic solids and high-viscosity slurries like paper pulp, a specialized valve referred to as a knife gate valve is used to cut via the cloth and prevent the waft. Unlike traditional wedge-fashioned gate valves, a knife gate valve has a tapered knife-like part on its decrease floor. In 1928, the first knife gate valve, referred to as the ‘Massaventil’ or Pulp stock valve / MV, become added by way of Mr. Canell and engineered by means of Stafsjö Valves AB in Sweden.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Gate Valve
Advantages Of Gate Valves
- The fluid resistance of gate valves is low. The instantly-through shape of the gate valve’s frame keeps the drift direction and allows for minimal resistance to fluid drift while completely open, making it more efficient than other valve kinds.
- Gate valves offer superior sealing performance compared to shut-off valves. The gate valve’s mechanism for establishing and final is quicker and more handy than that of close-off valves.
- Gate valves have a huge range of programs, consisting of steam, oil, and other media. They can also be used with granular solids and excessive viscosity media and may serve as each a venting valve and a low vacuum machine valve.
- Gate valves are bidirectional, bearing in mind waft in both guidelines. This makes them suitable for use in pipelines in which the go-with-the-flow route may change. Additionally, their easy design makes them simpler to put in than greater complex valve types.
Disadvantages Of Gate Valves
- Gate Valves Open & Close Slowly. The operation of Gate Valves is characterized with the aid of a sluggish establishing and last pace. This is because of the fact that during the opening technique, the valve plate needs to be lifted to the upper phase of the valve chamber, whilst for the duration of the last system, it should fall into the valve seat. As a result, the valve plate has to cover an extensive distance so as to complete those actions, resulting in an extended length for the hole and final technique. This disadvantage renders gate valves incorrect for programs that require rapid actuation.
- Gate Valves are at risk of scratches. The friction generated between the valve plate and the two sealing surfaces of the valve seat all through the hole and closing methods can cause scratches at the sealing surface. Although those scratches may seem insignificant, they can have a large effect on the sealing performance and carrier life of the valve. Repairing those damages isn’t always constantly an easy challenge, however, the installation and replacement of gate valves are exceptionally clean.
Related FAQ’S
When not to apply a gate valve?
Anaswer: Frequency of use: Since gate valves put on out faster, they’re frequently observed in applications in which they don’t need to be adjusted very frequently. Ball valves are recommended for applications that require frequent, quick manage over the drift of liquid.
What is the main use of gate valves?
Anaswer: Gate valves are used whilst an immediately-line drift of fluid and minimal drift restriction are needed. Gate valves use a sliding plate inside the valve body to stop, limit, or permit full go with the flow of fluids through the valve. The gate is typically wedge-fashioned.
Can gate valves fail to close?
Anaswer: When specifying a gate valve failure scenario, we’ve got three options: fail open to allow waft, fail near save you flow , and fail in the closing position. The first two options are energetic failure positions, while the 0.33 option is a passive failure position.
Why do gate valves leak?
Anaswer: Old and new valves can leak around the stem section, specifically while the valve deals with growing to become open or near the valve. Several reasons can cause this leakage: now not frequently completely final the valve, harm to the valve, terrible layout, and the use of the incorrect length gate valve.
Can a gate valve smash?
Anaswer: Gate valve repair: When a valve breaks within the closed position. In maximum cases, if a gate valve breaks in the closed role, gate valve restore paintings must be finished. Sometimes a shrink valve might be placed inside the sidewalk location. This would enable you to close the lessened valve and the water by way of the use of a scale-back field key.