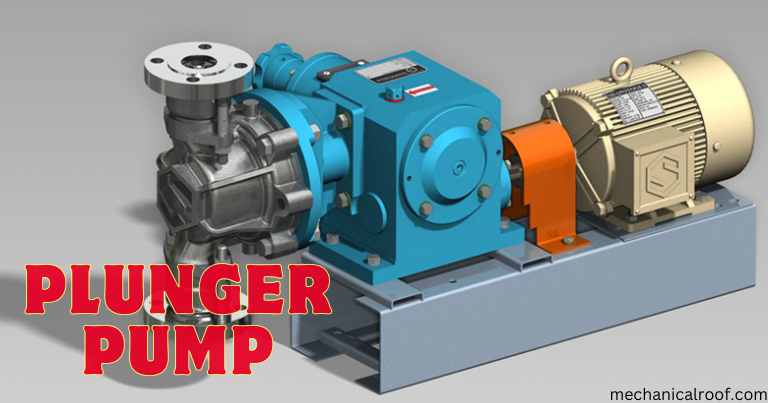
What Is Plunger Pump?
Plunger pumps are a type of positive displacement pump in which a high-pressure seal is set and a smooth cylindrical plunger pulls through the seal. This distinguishes it from piston pumps and allows it to be used at higher pressures. Such pumps are commonly used for municipal and industrial wastewater pumping.
Piston pumps, sometimes called piston pumps, have a plunger that moves back and forth, forcing water through a series of valves Some simple examples in our daily lives could be a bicycle pump, barrel sprayer, or a spray gun.
Commercially, plunger pumps are commonly used in cleaning, disinfection, pest control, agriculture, and other applications in their electrically driven devices such as pressure washers, atomizers, and sprayers Plunger pumps are attributed to Samuel Moreland based on a 1675 patent.
How Do Plunger Pumps Work?
Piston pumps and plunger pumps are reciprocating pumps that move medium through a cylindrical chamber through a plunger or piston. The plunger or piston is actuated by a steam-actuated, pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric actuator.
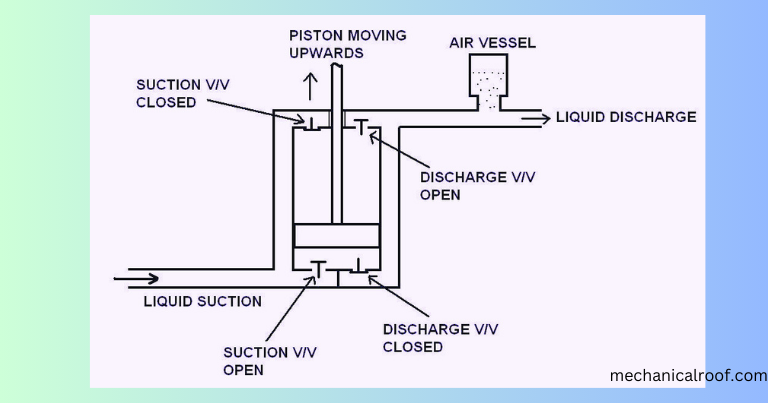
Rotary piston plunger pumps use a crank mechanism to create a reciprocating motion with the shaft, which then creates pressure in the cylinder or power cylinder and forces gas or water through the pump The pressure in the chamber supplies the valves to the suction and discharge points.
Piston pumps are used in applications from 70 to 2070 bar (1,000 to 30,000 psi). Piston pumps are used in low-pressure applications. The discharge volume is equal to the diameter of the plunger or piston times its stroke length.
The overall performance of piston pumps and plunger pumps can be calculated from the location of the piston or plunger, the stroke length, the number of pistons or plungers, and the speed of the drive The power demand of the drive is proportional to the pressure and the capacity of the pump.
The sealing of the piston pump and plunger pump is an important part of the separation of the driving fluid from the working fluid. A gland or packing is used to seal the plunger or piston connection of the container in which the medium is dispensed. The storage box can have bushings, packing or sealing rings, and a stuffing box.
The plunger pump is selected to hold the contents and communicate with the media type. Components include copper, brass, iron, stainless steel, iron, nickel alloys, or other materials. For example, plunger pumps in general service or oil service applications typically have a metal cylinder and plunger.
All ceramic plungers may be used during water-oil contact during operational operations with pistons, discharge valves, and suction valves in contact with the medium being transferred, and stopping water transfer a plunger pumps that continuously operate on selection materials required, but may not be suitable for use with highly acidic media.
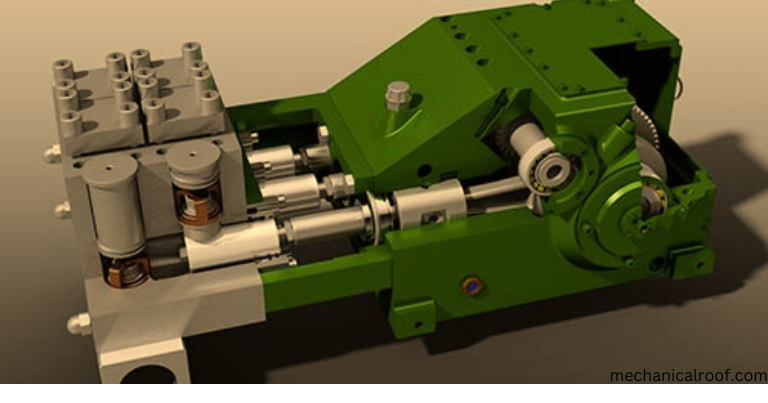
Applications Of Plunger Pumps
Plunger pumps can deliver high pressure. These pumps are capable of pumping heavier loads and more dense fluids. For these reasons, plunger pumps are used for the following applications.
- This pump is used for drug Injection.
- Consumption of oil and gas production
- A plunger pump is also used for gas dehydration
- Used to prepare for the page
- A plunger pump is used for drill-cutting injection
- Use it to harvest water
- These pumps are used for odor control and ventilation
- These pumps melt coal
- These are used for pressure testing
- Plunger pumps are also used to produce urea
- Cleaning agents are used
Plunger Pump Diagram
Differences Between Piston And Plunger Pumps
We discussed one by one piston pump and plunger punps:
Piston Pump
- An excessive-stress seal reciprocates with the piston in the cylinder.
- Best appropriate to quick obligation cycles until larger pump going for walks slowly.
- Inlet Design Pressure of 8.5psi to 40psi.
- Output pressure a 100-1200psi.
- Inlet valves mechanically actuated.
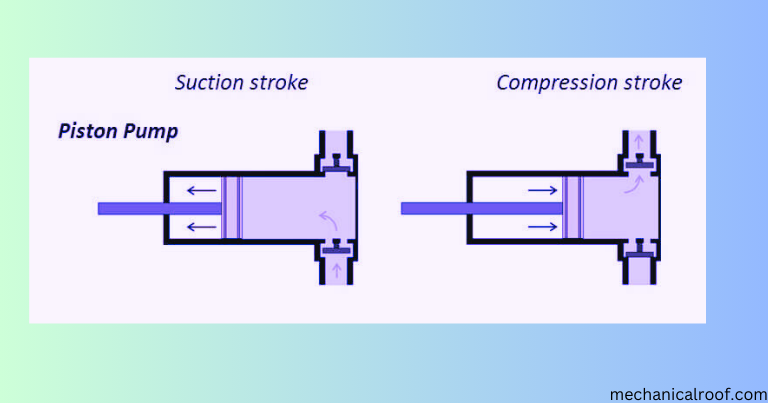
Plunger Pump
- The excessive-strain seal is desk-bound. The plunger slides through the seal allowing the pump to be used at better pressures.
- Requires flooded suction or better inlet strain supplied via a booster pump.
- OK for continuous operation whilst strolling slowly.
- Output pressure 100 to ten,000psi.
- Inlet design pressure of 60-70psi.

Advantages Of Plunger Pumps
- Has self-priming pump capability and is efficient.
- Very high generated/maintained pressure possible.
- Linear capacity control if variable speed is used.
- Leaks can be reduced without shutting down the pump if your company allows the packing to be tightened while the pump is running.
- These can produce higher pressures than piston pumps.
- Flow rate and pressure fluctuations are minimal.
- Effect on plunger pump performance.
- These can pump abrasives and slurries.
- These can move more complex and heavy loads.
Disadvantages Plunger Pumps
- Very low flow rate compared to centrifugal or axial pumps.
- Irregular movement of teeth causes throbbing.
- There is a tendency to cavitation due to the acceleration head, especially if the suction pipe is long.
- As such, there is more vibration due to reverse motion, although the rotational speed is. generally lower than for a dynamic pump.
- These pumps have high operating costs.
- These pumps require high maintenance costs.
- Plunger pumps cannot provide pulsating free flow.
- These pumps can handle only limited flows.
- These are large and heavy.
Related FAQ’s
What is the function of a plunger?
Answer: A plunger, a force cup, is a tool used by a plumber’s friend or a plumber’s assistant to remove clogs in drains and pipes. It is usually a rubber cup puller attached to a piece of wood (adhesive) made of wood or plastic. There is also a unique vine-like design, usually made of plastic.
How does a plunger pump work?
Answer: Rotary piston and plunger pumps use a crank mechanism to create a reciprocating motion with the axis, which then creates pressure in the cylinder or working cylinder and forces gas or water through the pump Pressure in the chamber moves the valves to suction and discharge points.
Why is the plunger not working?
Answer: Many homeowners find that the drains do not drain, and then simply plug in the plunger head and start running. However, if there isn’t enough water in the sink or toilet to fully submerge the plunger head, your efforts won’t be very effective.
Does a plunger always work?
Answer: However, a large or deep clog in your home’s plumbing may not be enough to handle the pressure of the plunger. Press the stopper without ever using too much force. If the drain doesn’t open by applying the right amount of pressure, you need the help of a professional. Forced submersion can cause drainage and dehydration.
How long does a plunger take?
Answer: To pass through water. Once your plunger is firm, place one or both hands on the handle. Press go up & down for 20 S. Take the plunger out of the drain using a straight upward motion.